With the growth of the internet, the dependence on computers has increased exponentially. The challenge is to protect critical information infrastructure, like the civil aviation sector, Railways‟ passenger reservation system and communication network, port management, companies and organizations in power, oil and natural gas sectors, banking and finance, telecom sector, etc. from cyber attacks.
The Biggest-Ever 3.8 Tbps DDoS Attack Aimed at International Sectors is Prevented by Cloudflare
A record-breaking distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) assault that peaked at 3.8 terabits per second (Tbps) and lasted 65 seconds has been successfully neutralized by Cloudflare. Over one hundred hyper-volumetric L3/4 DDoS assaults were thwarted by the web infrastructure and security business throughout the month, with many of them surpassing 2 billion packets per second (Bpps) and 3 terabits per second (Tbps). Numerous clients in the financial services, Internet, and telecommunications sectors were the targets of the attacks. No particular threat actor has been identified as the source of the activity.
Prior to November 2021, when it was directed at an unidentified Microsoft Azure customer in Asia, the highest volumetric DDoS assault record reached a peak throughput of 3.47 Tbps. Utilizing the User Datagram Protocol (UDP) protocol on a dedicated port, the assaults originate from Vietnam, Russia, Brazil, Spain, and the United States of America. These include DVRs, web servers, and hacked MikroTik devices. According to Cloudflare, a significant botnet made up of hacked ASUS home routers is probably the source of the high bitrate assaults. This botnet is likely being used to exploit a newly discovered major defect (CVE-2024-3080, CVSS score: 9.8).
The vulnerability may have affected more than 157,000 ASUS router models as of June 21, 2024; the majority of these units were found in China, Hong Kong, and the United States. The campaign’s ultimate objective is to consume up all of the target’s CPU time and network bandwidth, blocking access to the service for authorized users. Over the last four years, banking, financial services, and public utilities have experienced a 55% increase, and volumetric assaults have increased by 30% in the first half of 2024 alone. DDoS assaults have become more frequent, mostly due to hacktivist operations directed at international organizations and companies. DNS-over-HTTPS (DoH) is used to make detection more difficult for command-and-control (C2).
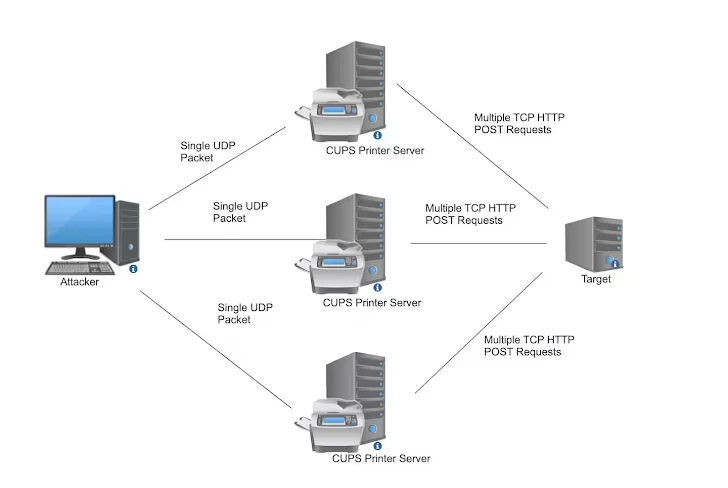
Akamai has shown Linux’s Common UNIX Printing System (CUPS) vulnerabilities to be a potential avenue for launching DDoS attacks with a 600x amplification ratio in a matter of seconds. According to the company’s investigation, over 58,000 of the approximately 198,000 devices that are available on the public internet can be used to launch DDoS assaults.
Why data security is critical to AI
Data is the new fuel. It powers innovation in technology, most notably generative AI, and our economy. But AI needs to be reliable and safe in order to be extensively used. Business interruptions drive breach costs and regulatory fines to unprecedented levels, as evidenced by the Data Breach Report, which indicates that the average cost of a data breach is USD 4.88 million.
However, over 94% of business executives agree that safeguarding AI is crucial, but just 24% said that their AI projects would contain a cybersecurity component over the next six months, according to a poll done for Business Value (IBV) research on cybersecurity and emerging AI.
This makes a lot of firms exposed since gen AI also introduces new dangers including rapid injection attacks, data poisoning, and data leaking.
It may be challenging for companies to manage who has access to their data. It’s critical to ensure that controls are in place to ensure that business and client data don’t get exposed. Businesses should set up their AI governance and secure their infrastructure—their data, models, and model usage—in order to protect their data and AI.
Businesses can begin this process by following these three steps:
Understand the data’s location: Many teams use Gen AI to develop quickly, but this might lead to the creation of “shadow IT.” “We need to make sure that companies are also visible. This will be aided by emerging technologies like AI security posture management and data security posture management.
Classify the data: various forms of data will have various ramifications and may be subject to distinct regulations and processes, regardless of whether you’re working with consumer or company data.
Implement classification limits: To assist in guaranteeing the correct people have access to the right data at the right time, apply the necessary restrictions to that data depending on the categorization limit, such as the customer data, the business data census, or publicly available data.
Practical Measures to Stop GenAI Data Leaks Without Completely Banning AI Use
Enterprise productivity has been changed by generative AI since its inception. Tools for artificial intelligence (GenAI) make company planning, financial analysis, software development, and customer interaction faster and more efficient. However there are serious hazards associated with this corporate agility, most notably the possibility of sensitive data leaks. Many firms are compelled to decide between allowing unfettered usage of GenAI or outright prohibiting it in an effort to strike a compromise between productivity improvements and security concerns.
In an effort to assist enterprises in navigating the obstacles associated with using GenAI in the workplace, LayerX has released a new e-guide titled 5 Actionable Measures to Prevent Data Leakage Through Generative AI Tools. The book provides security managers with doable actions to safeguard confidential company information while still maximizing the efficiency gains from GenAI solutions such as ChatGPT. This approach is intended to allow companies to strike the right balance between innovation and security.
Why Worry About ChatGPT?
The rising fear that unrestrained use of GenAI may result in accidental data leakage is addressed in the e-guide. As demonstrated, for instance, by events like the Samsung data breach. In one instance, workers utilizing ChatGPT unintentionally revealed proprietary code, which resulted in the corporation outright banning GenAI technologies. These kinds of occurrences highlight the necessity for businesses to have strong policies and controls in order to reduce the dangers related to GenAI.
In a report published by financial express they stated that “ChatGPT’s impact on the tech industry has been seismic since its launch, as it garnered one million users in just five days. This is an unprecedented feat, surpassing even leading social media platforms and microblogging sites. Its impressive capabilities have been widely reported, ranging from helping a Wharton professor clear an MBA exam to debugging and writing programming code, composing articles, stories, prose, music, solving math problems, doing translations, and more. The meteoric rise of ChatGPT has sparked concern among social media giants and the dominant search engine, which has become an integral part of our daily lives. Some reports suggest that the search engine has gone back to its founders in response to the threat posed by ChatGPT. Another e-commerce giant has instructed its employees to not share any confidential information with the AI chatbot.” Read full article here – https://www.financialexpress.com/life/technology/is-chatgpt-a-real-threat-to-humanity/2973166/
As per LayerX Security’s research:
15% of enterprise users have pasted data into GenAI tools. 6% of enterprise users have pasted sensitive data, such as source code, PII, or sensitive organizational information, into GenAI tools. Among the top 5 % of GenAI users who are the heaviest users, a full 50% belong to R&D.Source code is the primary type of sensitive data that gets exposed, accounting for 31% of exposed data
The following actions are some of the guide’s main highlights:
- Mapping AI Usage in the Organization- Recognize what needs to be protected first. Map who is using GenAI technologies, how they are using them, why they are using them, and what kinds of data they are exposing. This will serve as the cornerstone of a successful risk management plan.
- Restricting Personal Accounts- Next, take use of the security provided by GenAI products. The danger of sensitive data leaking may be considerably decreased with the built-in security features that corporate GenAI accounts offer. This covers constraints on the data that may be used for training, limitations on data preservation, limitations on account sharing, anonymization, and more.
- Prompting Users- Utilize the strength of your own workforce as a third stage. GenAI solutions can assist raise employee knowledge of business regulations and the possible repercussions of their conduct by displaying simple reminder messages. This can successfully cut down on dangerous conduct.
- Blocking Sensitive Information Input- It’s time to implement cutting edge technologies now. Put in place automatic safeguards that prevent sensitive data from being entered into GenAI products in big quantities. This works particularly well to stop employees from exchanging financial data, PII, source code, and customer information, among other things.
- Restricting GenAI Browser Extensions- Lastly, minimize the danger posed by browser extensions. AI browser extensions should be automatically managed and categorized according to danger in order to stop unwanted access to confidential company information.
Businesses must strike a balance between security and productivity if they hope to fully profit from generative AI’s productivity advantages. GenAI security therefore can’t be limited to either permitting or prohibiting all AI activities. Rather, businesses may profit from the commercial advantages without exposing themselves by adopting a more sophisticated and refined strategy. This is how security managers can become important business enablers and partners.




